Education
Types of Medical Negligence and How to Keep Safe?
Published
5 months agoon
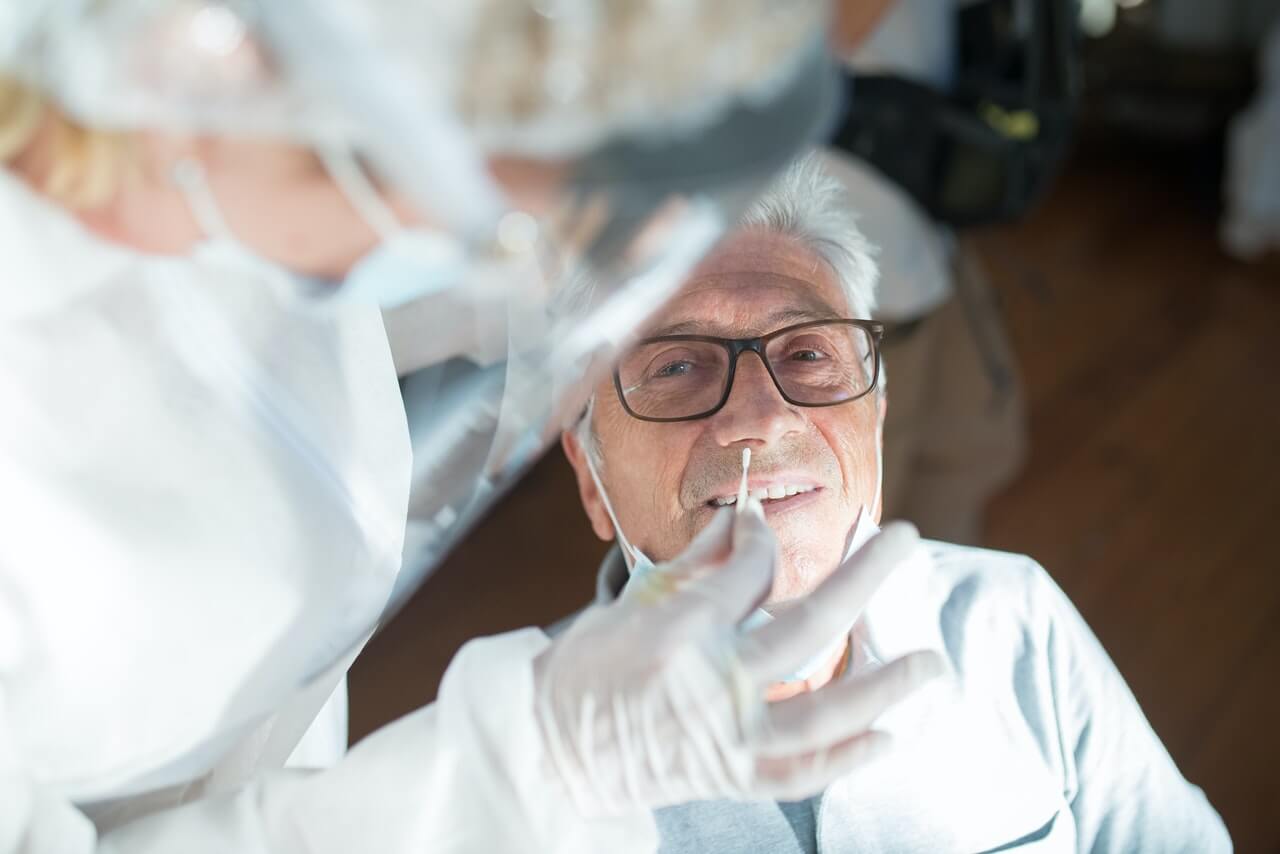

Medical Negligence
Navigating the realm of healthcare involves placing trust in the expertise of medical professionals.
However, instances of medical negligence, where the standard of care is not met, can have serious consequences for patients.
This article explores various types of medical negligence that individuals may encounter, shedding light on common scenarios such as misdiagnosis, surgical errors, medication mistakes, and more.
Understanding these types of negligence is crucial for patients to advocate for their own safety.
Additionally, practical tips on how to stay safe within the healthcare system will be discussed, empowering individuals to be proactive in their healthcare journey and foster a sense of awareness and well-being.
What is Medical Negligence?
Medical negligence can take various forms, and some common examples include misdiagnosis, surgical errors, medication errors, birth injuries, anesthesia errors, infections or hospital-acquired conditions, and lack of informed consent.
These instances may result from a healthcare provider’s actions, omissions, or failure to adhere to established medical standards. To establish a case of medical negligence, certain elements typically need to be demonstrated:
- Duty of Care: The healthcare provider owed a duty of care to the patient.
- Breach of Duty: The provider breached the standard of care through negligent actions or omissions.
- Causation: The breach of duty directly caused harm or injury to the patient.
- Damages: The patient suffered damages, such as physical or emotional harm, as a result of the breach of duty. It’s important to note that not all unfavorable outcomes in medical treatment are considered medical negligence.
Medicine involves inherent uncertainties, and not every medical error qualifies as malpractice. However, when negligence is evident and results in harm to the patient, legal recourse may be pursued through a medical malpractice lawsuit.
Patients who believe they have experienced medical negligence should seek legal advice promptly. Consulting with a medical malpractice attorney can help determine if there are grounds for a case and guide individuals through the complex legal process.
Common Types of Medical Negligence
Medical negligence refers to situations where healthcare providers fail to meet the standard of care expected in their profession, leading to harm or injury to patients.
Several types of medical negligence can occur, and understanding them can help individuals advocate for their own safety.
Here are some common types of medical negligence and tips on how to stay safe:
Misdiagnosis or Delayed Diagnosis
Misdiagnosis occurs when a healthcare professional provides an incorrect diagnosis, while delayed diagnosis involves a significant delay in diagnosing a medical condition. To stay safe, ask questions about your diagnosis, seek a second opinion if needed, and communicate openly with your healthcare team.
Surgical Errors
Surgical errors encompass a range of mistakes during surgery, such as performing the wrong procedure, operating on the wrong body part, or leaving instruments inside the patient. Patients can reduce the risk by clearly verifying details before surgery, understanding the procedure, and maintaining open communication with the surgical team.
Medication Errors
Medication errors involve mistakes in prescribing, dispensing, or administering medication. Patients should ensure that healthcare providers are aware of their allergies, confirm the prescribed medication, and ask about potential side effects. It’s essential to keep an updated list of medications and share it with all healthcare providers.
Birth Injuries
Birth injuries may occur during childbirth due to medical negligence. Expectant parents can attend prenatal classes, discuss birth plans with healthcare providers, and ask questions about potential complications. Open communication with the medical team is crucial during labor and delivery.
Anesthesia Errors
Anesthesia errors involve administering too much or too little anesthesia, leading to complications. Patients can reduce risks by providing accurate medical histories, discussing concerns with the anesthesiologist, and following pre-surgery fasting guidelines.
Infections and Hospital-Acquired Conditions
Infections and hospital-acquired conditions may result from inadequate sanitation or hygiene practices. Patients can protect themselves by practicing good hand hygiene, asking healthcare providers to wash their hands, and being proactive in preventing infections.
Lack of Informed Consent
Lack of informed consent occurs when patients are not adequately informed about the risks and benefits of a medical procedure. Patients should actively participate in their healthcare decisions, ask questions, and ensure they fully understand the implications of any proposed treatment.
What To Do In Case of Medical Negligence?
Experiencing medical negligence can be distressing, but taking prompt and informed actions is crucial. Here are steps to consider if you believe you’ve been a victim of medical negligence:
- Seek Immediate Medical Attention: If you’re experiencing adverse effects from medical treatment, seek immediate medical attention to address and document any complications. Your health is the top priority.
- Document Everything: Keep detailed records of your medical treatment, including dates, names of healthcare providers involved, prescribed medications, and any symptoms or issues you’ve experienced. Documentation will be valuable when assessing the situation later.
- Speak with the Healthcare Provider: If you’re comfortable doing so, communicate your concerns with the healthcare provider directly. Sometimes, misunderstandings can be clarified, and corrective actions may be taken.
- Contact the Healthcare Facility: Report the incident to the healthcare facility where the negligence occurred. Hospitals and clinics often have procedures in place for handling patient concerns and complaints.
- Contact a Medical Solicitor: Consult with a medical solicitor who specializes in medical negligence cases. They can assess the details of your situation, determine the viability of a legal claim, and guide you through the legal process.
- Complain to Regulatory Bodies: Report the incident to relevant regulatory bodies overseeing healthcare professionals. In the UK, you can contact organizations such as the General Medical Council (GMC) or the Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC).
- Keep Communication Records: Maintain records of all communications related to the incident, including emails, letters, and phone calls. This documentation can be valuable in legal proceedings.
Conclusion
By fostering open communication with healthcare providers, seeking second opinions, and actively participating in treatment decisions, individuals can play a proactive role in their own safety.
Likewise, healthcare professionals must continually uphold the highest standards of care, recognizing that patient safety is a shared responsibility.
Through a collaborative effort between patients and providers, we can work towards a healthcare landscape where negligence is minimized, trust is fortified, and the well-being of all is prioritized.

Trending

 Banco4 years ago
Banco4 years agoBanjercito

 Gaming3 years ago
Gaming3 years agoNBA 2K21 Best Controller Settings
 Social Media3 years ago
Social Media3 years agoHow to prepare a publication schedule

 Indonesia4 years ago
Indonesia4 years agoSerial Number CorelDraw X7 Aktivasi Kode 64/32 Bit | Dijamin Bisa

 Filmora4 years ago
Filmora4 years agoWondershare Filmora 9 Activation Key and Email Free 2020

 Education1 year ago
Education1 year agoJuan Monteverde on the Unexpected Costs of Corporate Fraud
 Indonesia3 years ago
Indonesia3 years agoMangastream – 15 Alternatif Terbaik untuk Membaca Manga Online [2021]

 Education4 years ago
Education4 years ago28 Best Bane Quotes From The Movie “The Dark Knight Rises”
You must be logged in to post a comment Login