Business
What You Need to Know About Business Formation Law
Published
1 year agoon
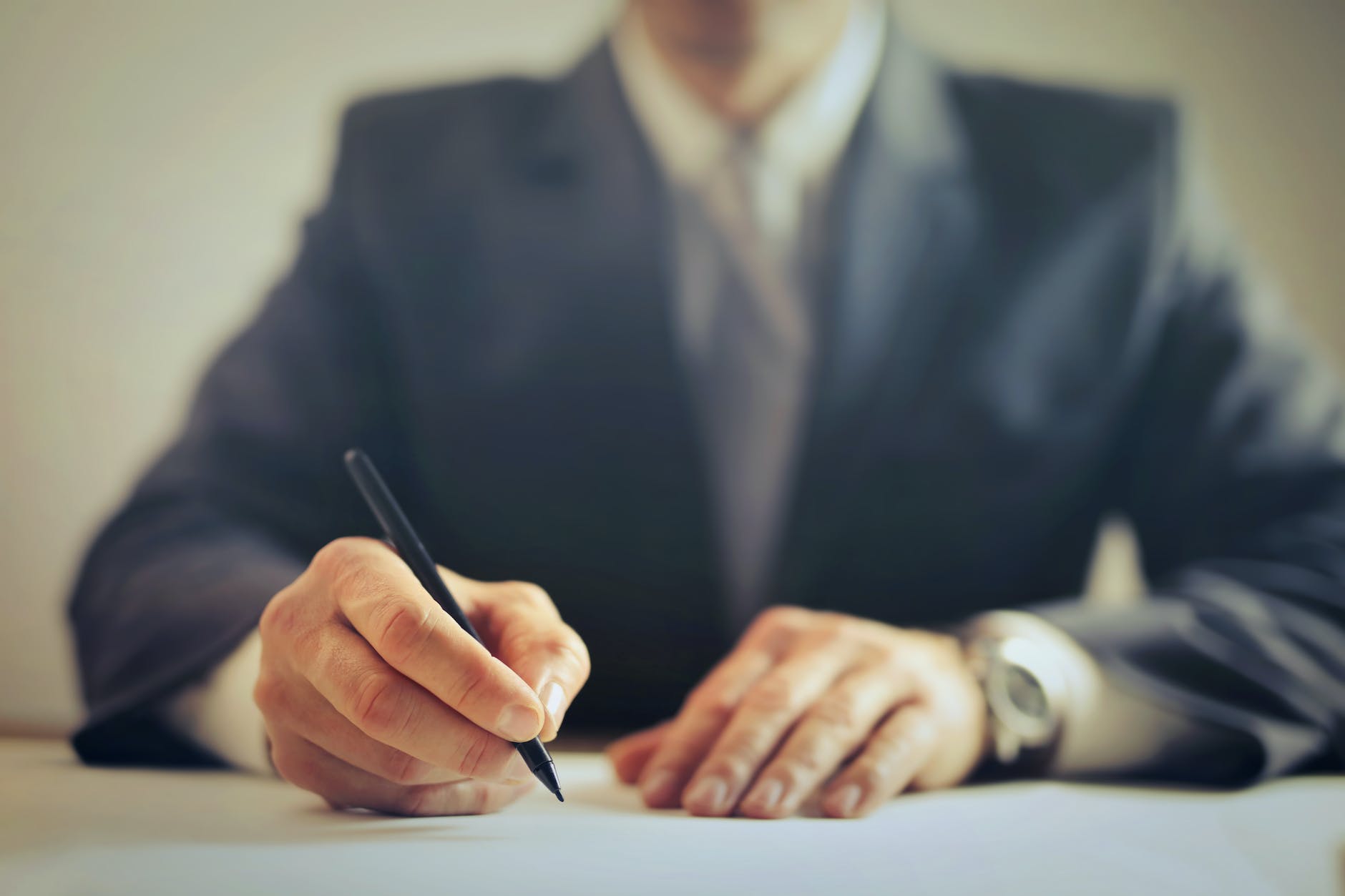

What You Need to Know About Business Formation Law
Before you start your business, you need to know about Business Formation Law. The type of business you have will determine what paperwork you need to complete and how much funding you need. A qualified Business Formation Lawyer will be able to guide you through the process. The Blake & Ayaz team has over 60 years of experience and can help you form a corporation, turn an idea into a legal entity, and represent you in any legal disputes you may have.
Corporations
In the United States, corporations are entities created to carry out a business. They have an elected board of directors, who make decisions that affect the shareholders and formulate policies for management. They must act in the best interest of the corporation and its shareholders. Corporations can own properties, conduct business, and enter into binding contracts.
A business corporation must designate the number of shares it will issue in its certificate of incorporation, and must state its par value. Shares without a specified par value may be sold for any price, but shares with a stated par value cannot be sold below the value of the corporation. This can help protect shareholders.
Corporations are the most widely recognized form of business entity. They can offer limited liability to owners and access to a variety of financial resources. They don’t suffer from double taxation and can protect the owners’ personal assets from business debts.
Limited liability companies
Limited liability companies are companies in which the owners are limited in their liability. The company must have at least one shareholder and must be formed under the laws of the state in which it is located. In addition, the company must be registered with the state Department of Corporations. The federal government has specific laws that apply to this type of entity.
One of the benefits of an LLC is that it is subject to fewer regulations than a traditional corporation. It also allows members to have a more flexible management structure. However, the flexibility of LLC members is primarily determined by the LLC’s operating agreement. While state statutes usually provide default rules for LLCs, an operating agreement allows members to amend or change the rules of an LLC.
Although there are differences between LLCs and partnerships, both have the same basic structure. In an LLC, the members of the company may transfer economic rights to a third party but may not transfer other rights. LLCs are similar to state-law partnerships but have important differences.
Partnerships
In business formation law, a partnership is an organization with two or more owners that engage in a business together for profit. The default rule is that all partners share an equal amount of ownership in the business. This can be changed only by formal written agreement. In addition, each partner has an equal say in management decisions and is liable for all debts and torts committed by the business.
One of the main advantages of a partnership is that it is inexpensive to operate. Unlike corporations, partnerships have fewer requirements for record-keeping and reporting, but they must still abide by the same taxation requirements. These obligations are outlined in IRS publication 583. In addition, partners must adhere to other legal obligations as a small business, including compliance with state and federal regulations.
There are several different types of partnerships. The most common type is the limited partnership, which can be formed between two or more people. The partners can run the business alone, or employ employees and independent contractors. A partnership is usually created through a formal agreement, which outlines the capital contributions required of each partner, how the business is managed and how profits are allocated.
Sole proprietorships
Sole proprietorships are a unique business structure. Unlike a corporation or LLC, a sole proprietor pays personal income taxes on profits and business losses. This is why many people prefer sole proprietorships. This type of business structure also allows an owner to choose a fictitious name for their business, called a “Doing Business As” name. This name makes it easier for customers to identify the business.
The process to establish a sole proprietorship is relatively simple. It involves filing a DBA, acquiring a business license, and acquiring local licenses. However, this type of business does have some special considerations that make it more difficult to register in the state that you reside in.
Sole proprietorships are the most common business formation type. The business owner is 100% responsible for managing the business. In addition, there is no legal distinction between the business and its owner, so a sole proprietor is responsible for all business debts and liabilities. In addition to this, a sole proprietorship is subject to pass-through taxation, which means that the owner pays taxes on the business’s income on their personal tax return. Sole proprietorships are also subject to unlimited personal liability, although the owner can mitigate this risk with insurance and sound contracts.

Trending

 Banco4 years ago
Banco4 years agoBanjercito

 Gaming3 years ago
Gaming3 years agoNBA 2K21 Best Controller Settings
 Social Media3 years ago
Social Media3 years agoHow to prepare a publication schedule

 Indonesia4 years ago
Indonesia4 years agoSerial Number CorelDraw X7 Aktivasi Kode 64/32 Bit | Dijamin Bisa

 Filmora4 years ago
Filmora4 years agoWondershare Filmora 9 Activation Key and Email Free 2020

 Education1 year ago
Education1 year agoJuan Monteverde on the Unexpected Costs of Corporate Fraud
 Indonesia3 years ago
Indonesia3 years agoMangastream – 15 Alternatif Terbaik untuk Membaca Manga Online [2021]

 Education4 years ago
Education4 years ago28 Best Bane Quotes From The Movie “The Dark Knight Rises”
You must be logged in to post a comment Login